Inindustrial steam systems, especially in power generation, petrochemical and process industries, the temperature and quality of the steam is critical. The steam produced is often in the form of”superheated steam”. However, some processes require saturated steam or a vapor form close to it. This is where superheated steam coolers, or desuperheaters, come into play.
So why is superheated steam cooled, what is a desuperheater and how does it work? Let’ s examine it together.
What issuperheated steam?
Superheated steam is a type of steam heated above the saturation temperature, completely in the gas phase without liquid water droplets. Generally, after leaving the steam boiler, it is raised to higher temperatures with systems such as economizer and superheater.
Example: At a pressure of 10 bar , the saturated steam temperature is about 184 °C. Superheated steam can be above this value, for example 250 °C.
Although superheated steam offers advantages in terms of energy transportation and turbine efficiency, it cannot be used directly in some processes due to its low heat transfer efficiency.
Desuperheater Nedir?
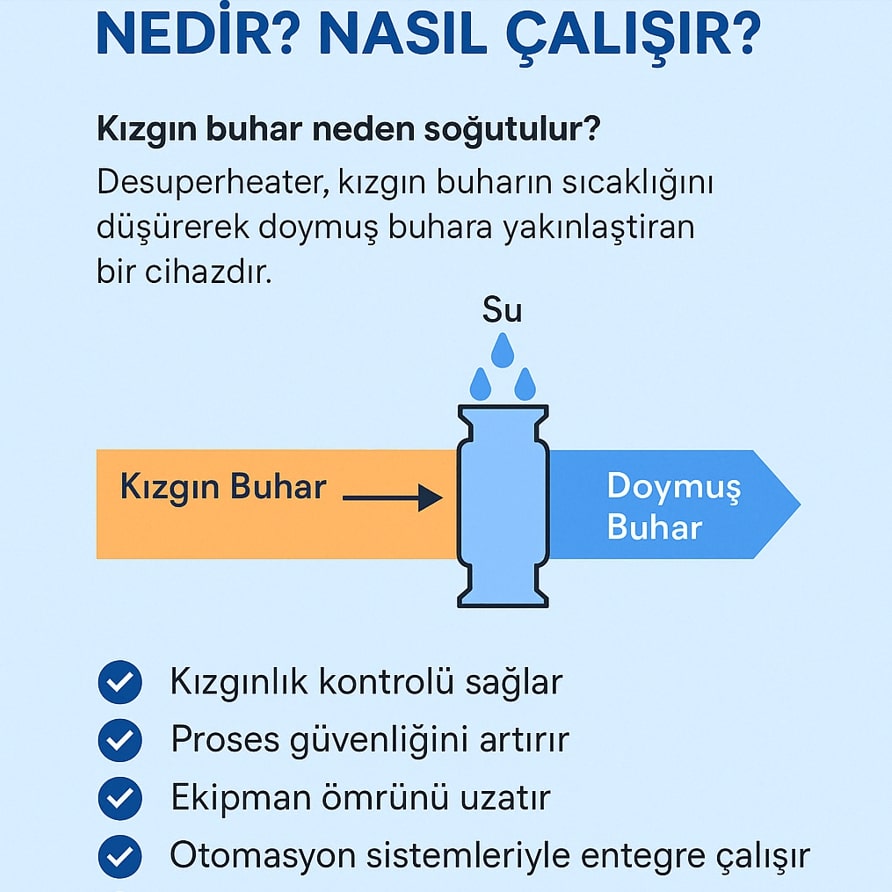
Desuperheater is a piece of equipment that reduces the temperature of superheated steam, bringing it closer to the saturated steam temperature or reducing it completely to the saturation point. Its main purpose is to produce steam suitable for the process requirement by reducing superheat.
This is usually accomplished by inject ing water directly into the steam line. This reduces the temperature and ensures process safety.
How doesthe Desuperheater work?
🔧 Basic Working Principle:
-
The high temperature steam from the superheated steam line enters the desuperheater.
-
The system sprays a controlled amount of water into the superheated steam (spray nozzle, venturi, etc.).
-
When this water comes into contact with steam, it evaporates rapidly and thus lowers the temperature of the steam.
-
The vapor is sent to the system close to the saturated vapor temperature or reaching the desired temperature value.
Desuperheater Technical Specifications
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Temperature | +150 °C to +600 °C |
| Pressure Range | 1bar – 100 bar |
| Coolant | Feedwater / Condensate |
| Control Type | Automatic (PID controlled), Manual |
| Type Options | Spray type, Venturi type, Combination |
| Material Options | Carbon steel, Stainless steel, Alloy steel |
Desuperheater Türleri
Desuperheater systems can vary in design and application:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Spray Tipi Desuperheater | It sprays water in fine particles with nozzles. Provides fast and controlled cooling. |
| Venturi Tipi Desuperheater | Water mixes better with steam by increasing the steam velocity. High efficiency. |
| Spray & Venturi Combination | Used in processes requiring high precision. The most advanced type. |
| Desuperheater + Control Valve | The injection amount is automatically adjusted according to the process conditions. |
Why Superheated Steam is Cooled?
-
🔹 Lower temperature may be required according to process needs
-
🔹 Heat transfer surfaces need to be protected (e.g. heat exchangers)
-
🔹 To increase device and equipment lifetime
-
🔹 For the efficient operation of control systems
-
🔹 For energy saving and safety
Areas of Use
Desuperheaters are widely used in the following sectors:
-
⚙️ Power plants (before or after steam turbine output)
-
🏭 Chemical and petrochemical plants
-
🧪 Process industries (food, textile, paper, etc.)
-
💧 Steam-based heating systems
-
🚿 Condensate recovery systems
Advantages
✅ Precisely controls superheat
✅ Improves process safety
✅ Extends equipment life
✅ Energy efficient
✅ Can be integrated with automation systems
Evaluation
Superheated steam coolers are indispensable for temperature control in industrial steam systems. Providing the appropriate steam characteristics for the process requirements plays a critical role in terms of system safety, efficiency and equipment health. Especially in applications where controlled steam temperature is required, a properly selected desuperheater provides both energy savings and operational success.